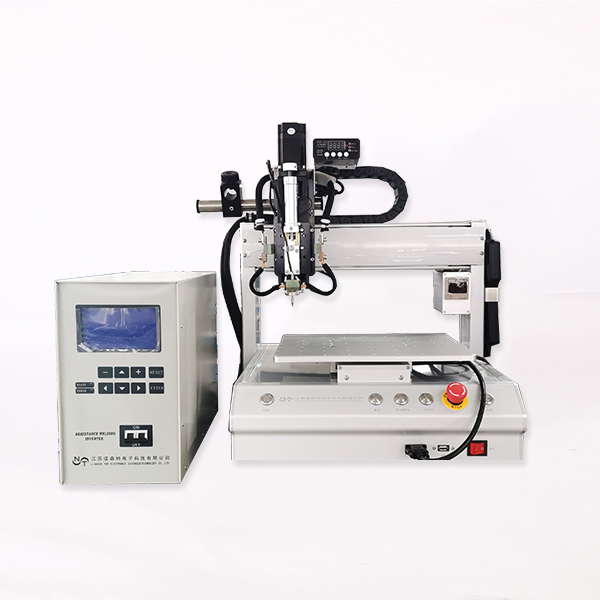
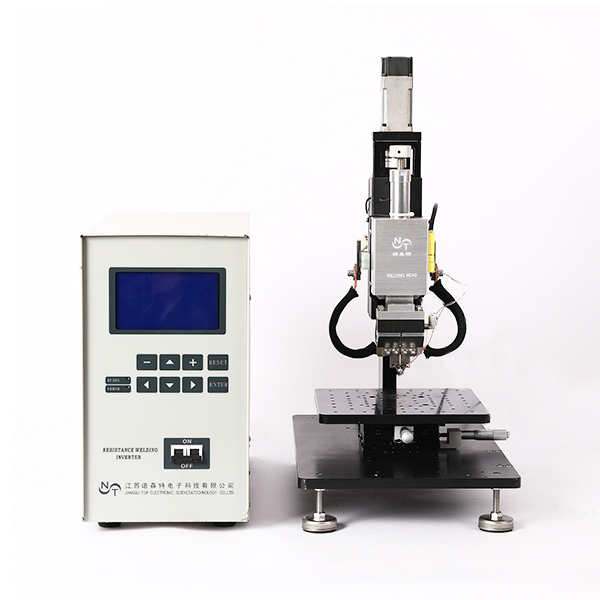
Principle of resistance welding machine
Resistance welding machine is to weld metal and metal together. It is composed of a welding head holding metal and applying pressure and a welding power supply outputting current.
Resistance is the resistance opposite to the direction of travel, similar to the heating phenomenon caused by friction when braking. When the same current flows in two metals, the resistance of the metal itself and the resistance of the contact part will generate heat. Resistance welding uses this Joule heat and pressure to weld metals together.
Composition and function of resistance welding machine
Resistance welding is to hold the object to be welded with electrodes, apply pressure and power on at the same time.
Welding power supply: control the size, time and waveform of welding current.
Welding transformer: change the current controlled by power supply into large current.
Welding head: control pressure.
Welding electrode: apply pressure and power to the welded object.
Temperature distribution of resistance welding

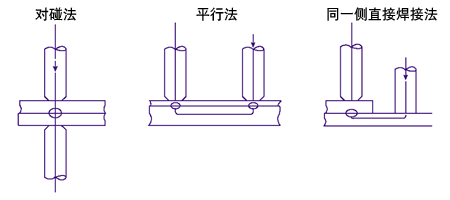
Power on mode of welding current
Generally, there are three kinds of methods to determine the welding current from the shape of the welding object. In addition, different pressure is applied to different methods of power on, and the corresponding welding joints are selected accordingly.
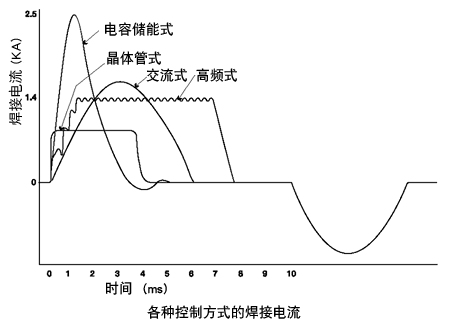
The type and specialty of resistance welding power supply refer to the device controlling welding current. According to the control mode, it can be divided into four types: high frequency type, transistor type, capacitor energy storage type and AC type, corresponding to a variety of welding objects.
|
Characteristics / forms
|
Alternating current
|
Capacitor energy storage type
|
Transistor type
|
High frequency type
|
|
Welding spark prevention |
○ |
△ |
◎ |
◎ |
|
Stability in case of power supply change |
△ |
◎ |
◎ |
◎ |
|
Welding efficiency |
○ |
△ |
△ |
◎ |
|
Feedback control |
no |
no |
yes |
yes |
|
Speciality |
Copper wire, plate |
Small thermal impact |
Micro components |
Non sparking welding |
Welding parameters and conditions
Selection of welding parameters: generally determined by the following three variables.
Welding current or voltage, power
Welding time
pressure
In addition, factors determining the welding quality
Shape of welding material
Dimensions of welding materials
Coating material and thickness of welding materials
Electrode material and shape
Ideal welding power supply and selection of welding head
 Taobao1
Taobao1 Taobao2
Taobao2 Alibaba Wuxi
Alibaba Wuxi Shenzhen Alibaba
Shenzhen Alibaba
 English
English Chinese
Chinese





